0102030405
Understanding RO Membrane Housing
2024-05-31
Key Components
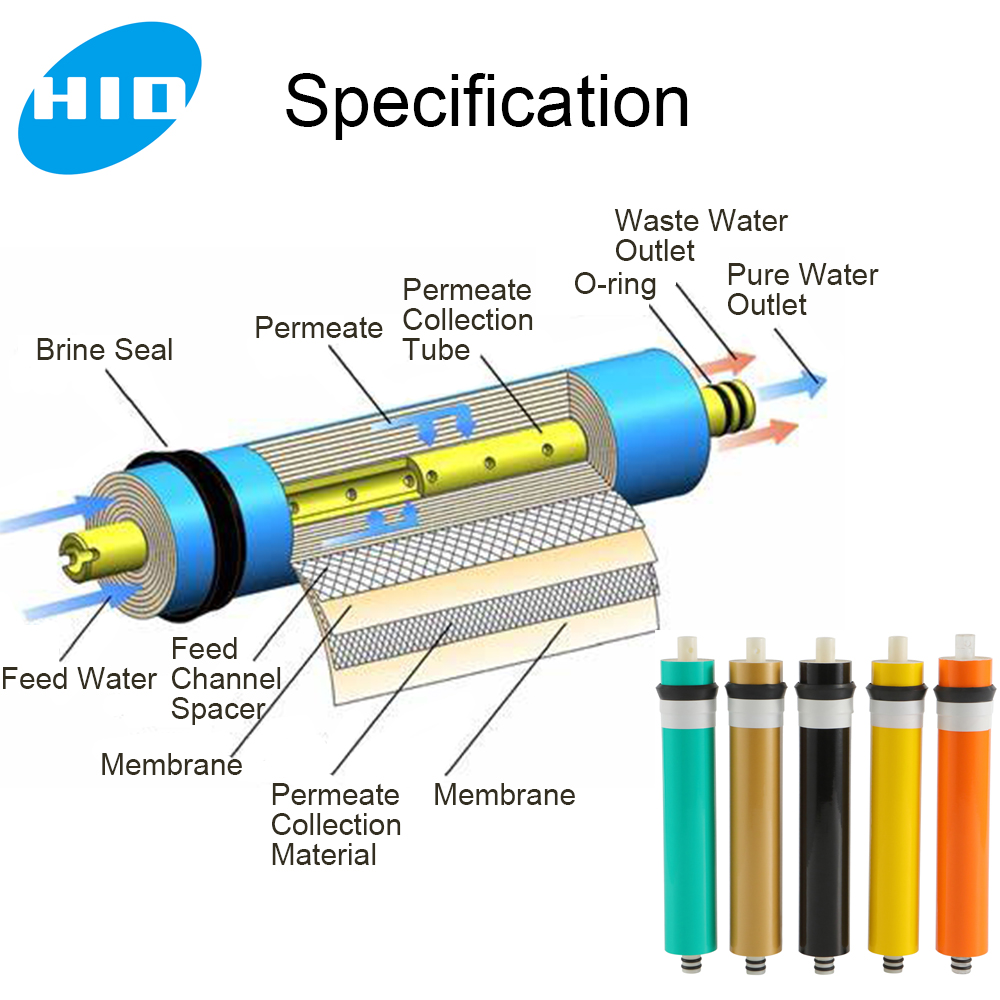
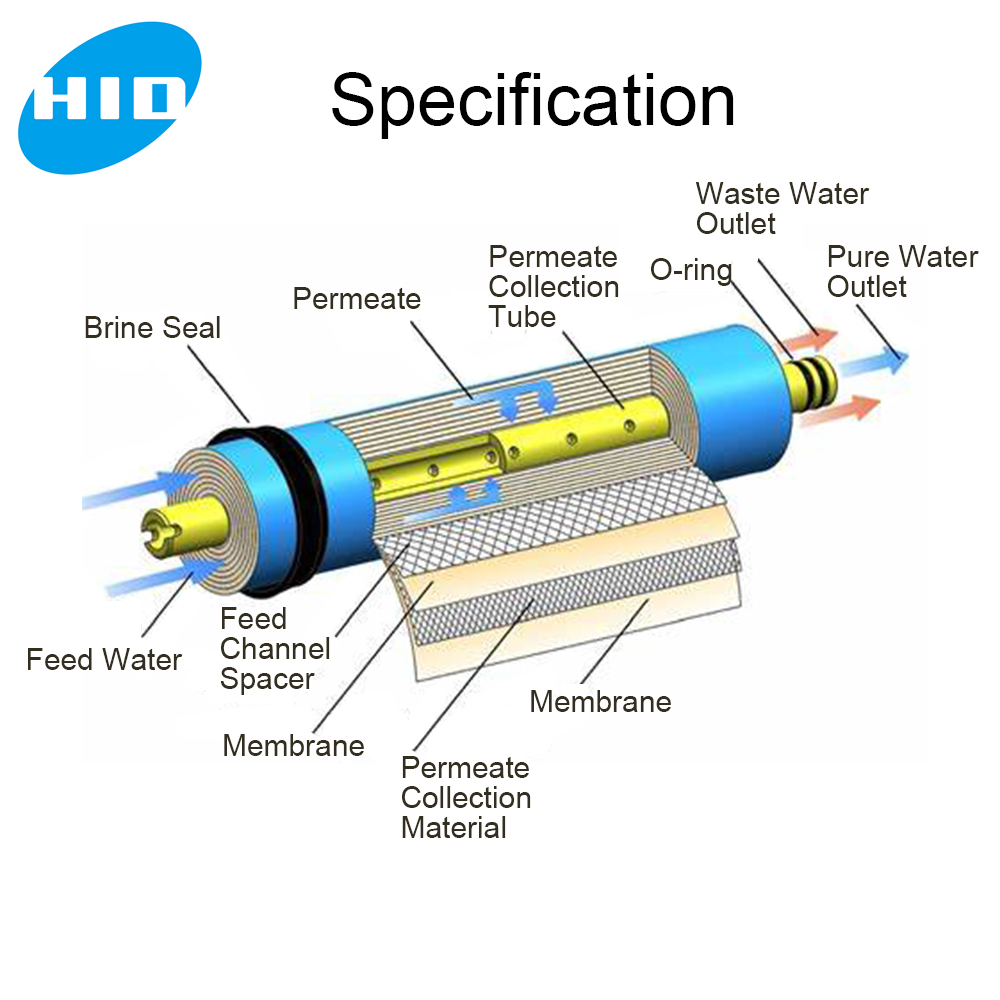
- Membrane Housing Tube: The cylindrical or spiral-shaped housing that encloses the RO membrane. It provides structural support and ensures proper sealing.
- End Caps: These are attached to the membrane housing tube and serve as the entry and exit points for water flow.
- O-Rings or Seals: These prevent water leakage by creating a tight seal between the end caps and the housing tube.
- Pressure Vessel: The entire assembly, including the housing tube, end caps, and seals, is often referred to as the pressure vessel.
- Inlet and Outlet Ports: These allow water to enter and exit the housing.
Functions of RO Membrane Housing
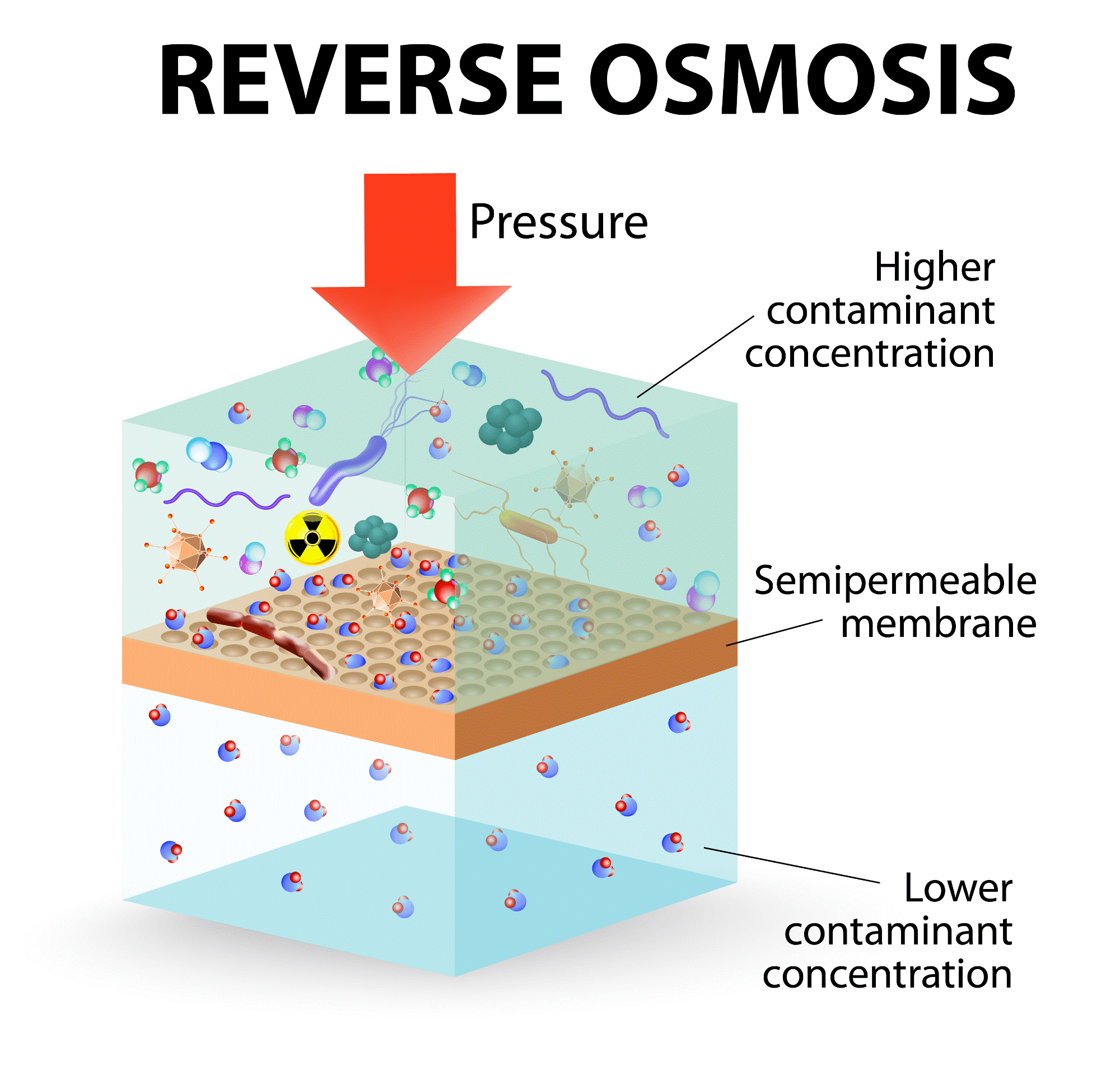
- Protection: The housing shields the delicate RO membrane from physical damage, debris, and external contaminants.
- Pressure Regulation: It maintains the necessary pressure inside the membrane housing to optimize filtration efficiency.
- Sealing: Properly sealed housing prevents leaks and ensures efficient water flow through the membrane.
Material and Design
- Materials: RO membrane housings are typically made of durable materials such as stainless steel, fiberglass-reinforced plastic (FRP), or polypropylene
- Design: The design can be either vertical or horizontal, depending on the system configuration.

Installation and Maintenance
- Installation:
- Position the housing vertically or horizontally based on available space.
- Attach the end caps securely.
- Insert the RO membrane into the housing.
- Ensure proper alignment of O-rings or seals.
- Connect the inlet and outlet ports to the water supply.
- Regularly inspect the housing for cracks, leaks, or signs of wear.
- Replace damaged O-rings promptly.
- Clean the housing interior during membrane replacement.
- Follow manufacturer guidelines for maintenance intervals.
What are common maintenance issues with housing?
- Leaking O-Rings or Seals:
- Issue: O-rings or seals can degrade over time, leading to leaks around the end caps.
- Solution: Regularly inspect and replace damaged O-rings or seals. Lubricate them with food-grade silicone grease to maintain a tight seal.
- Issue: Physical damage to the housing (such as cracks or dents) can compromise its integrity.
- Solution: Inspect the housing periodically for any signs of damage. Replace it promptly if you notice cracks or other issues.
- Issue: Biofilm (bacterial growth) or fouling (accumulation of organic matter) can occur inside the housing, affecting water quality.
- Solution: Regularly clean the interior of the housing during membrane replacement. Use approved cleaning solutions to prevent biofilm buildup.
- Issue: Minerals and scale deposits can accumulate on the membrane housing, reducing water flow and efficiency.
- Solution: Clean the housing using mild acid solutions (such as citric acid) to remove scale. Follow manufacturer guidelines for cleaning frequency.
- Issue: Incorrect pressure inside the housing can impact filtration efficiency.
- Solution: Monitor pressure using a pressure gauge. Adjust it within the recommended range (usually 10-20 psi) to optimize performance.
- Issue: Poor ventilation can lead to heat buildup inside the housing.
- Solution: Ensure proper spacing around the housing to allow air circulation. Avoid placing it near heat sources.
- Issue: Using incompatible cleaning chemicals can damage the housing material.
- Solution: Use only approved cleaning agents and follow guidelines provided by the manufacturer.
RO membrane housing is the unsung hero of reverse osmosis systems, safeguarding the heart of the purification process—the RO membrane. Next time you enjoy a glass of crystal-clear water, remember the critical role played by this unassuming housing!