Principle of Reverse Osmosis Application
Basic Principle of Reverse Osmosis:
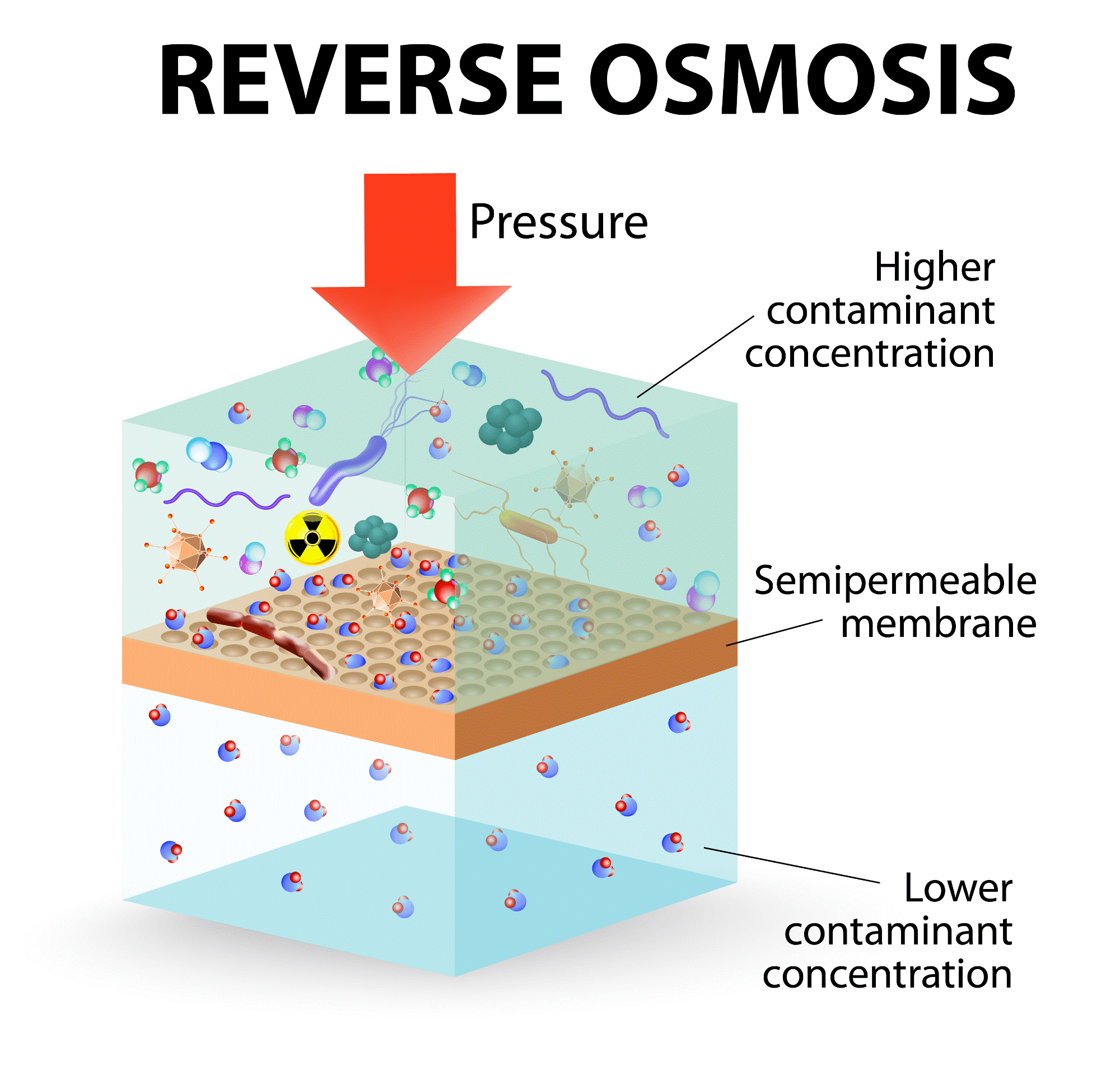
Reverse osmosis (RO) is a process where water flows from a side of low concentration (dilute solution) to a side of high concentration (concentrated solution) under the influence of applied pressure.
The RO membrane has extremely small pores (typically around 0.0001 micrometers), allowing only water molecules and certain beneficial ions to pass through.
Impurities, dissolved salts, and heavy metals are effectively rejected by the membrane and are discharged as reject water or brine.
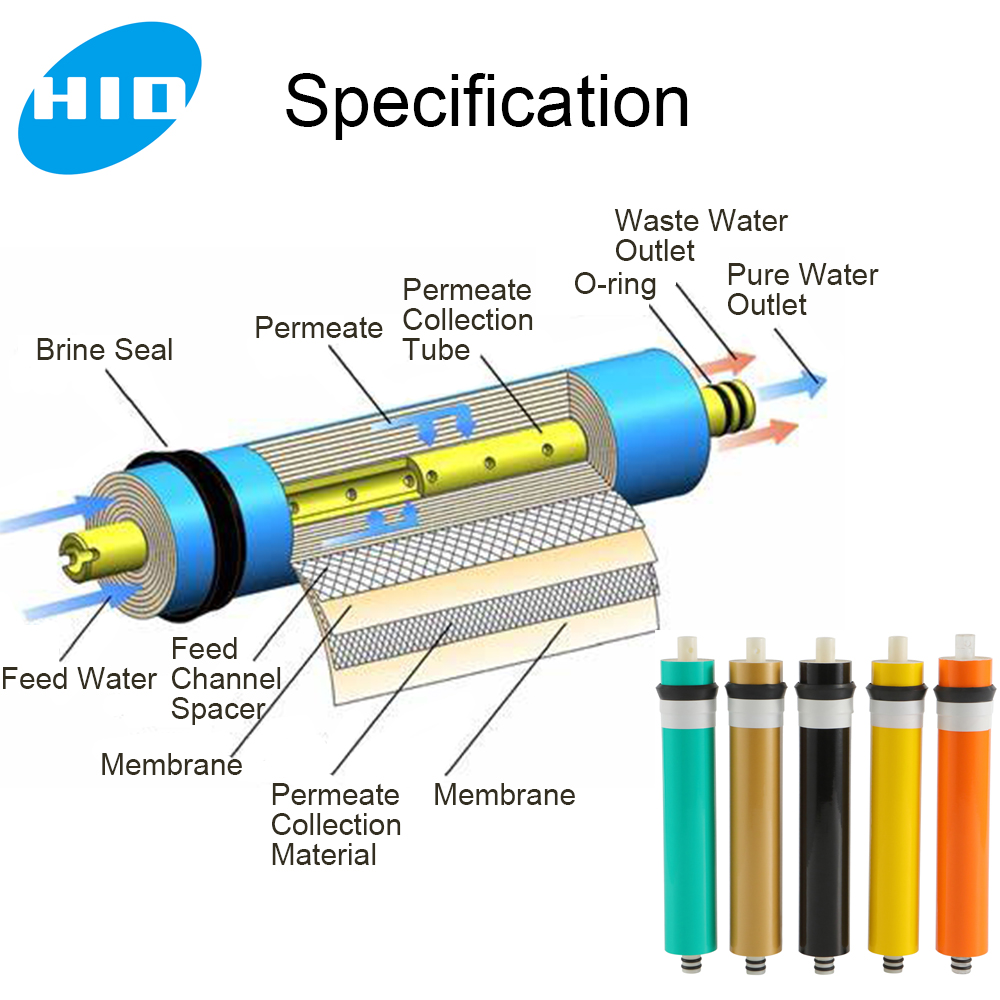
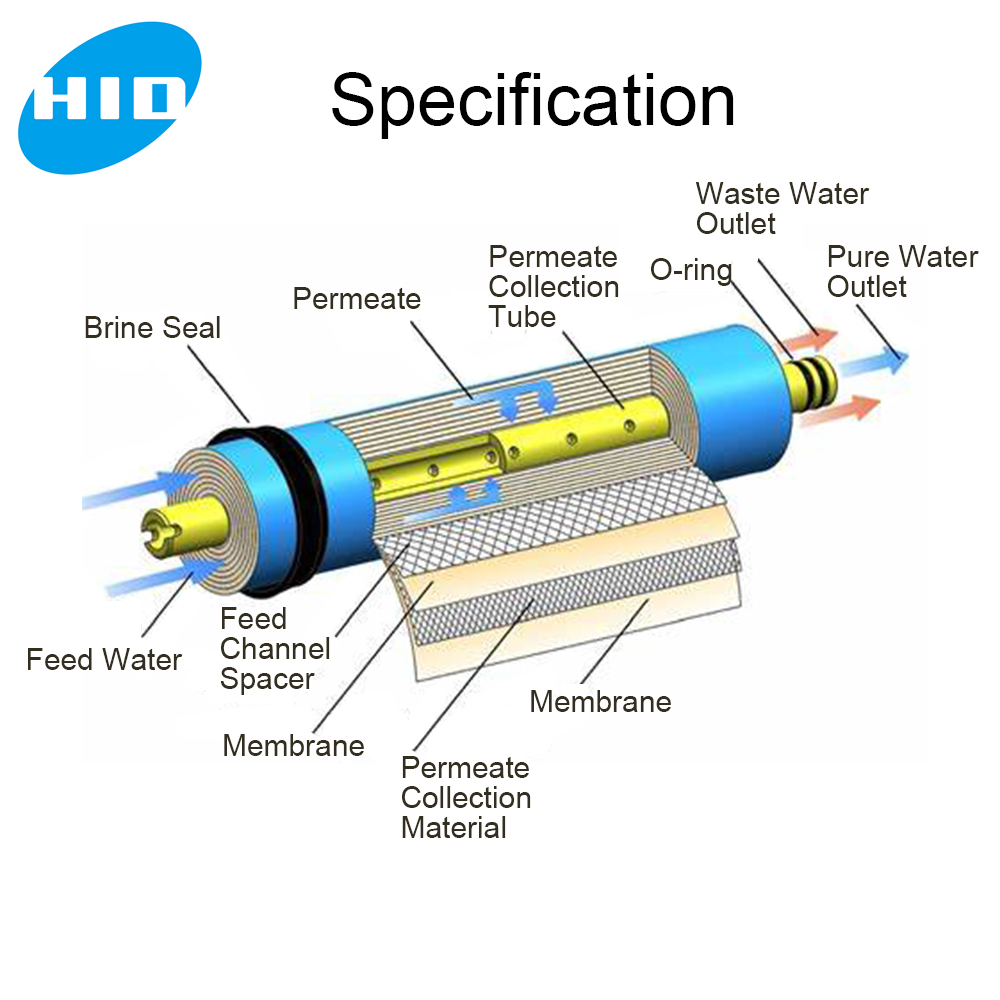
RO Membrane Structure and Working:
The RO system consists of an outer membrane housing and an internal spiral-wound RO membrane.
The RO membrane is composed of multiple layers, including end caps, a central tube, O-ring seals, the RO membrane itself, and inlet/outlet mesh screens.
Water passes through the layers of the RO membrane under pressure, allowing water molecules to permeate while retaining impurities.
The resulting purified water (product water) is collected, while the concentrated impurities remain on the feed water side.
Key Performance Parameters of RO:
Salt Rejection (Desalination Rate): Indicates the membrane’s ability to remove salts. Higher salt rejection indicates better performance.
Water Production Rate (Flux): The amount of water produced per unit time (usually measured in tons per hour).
Recovery Rate: The percentage of feed water converted into product water. Optimal recovery rates balance water conservation and membrane lifespan.
Reverse osmosis (RO) membrane technology is widely used in various fields. Here are some key applications of reverse osmosis:
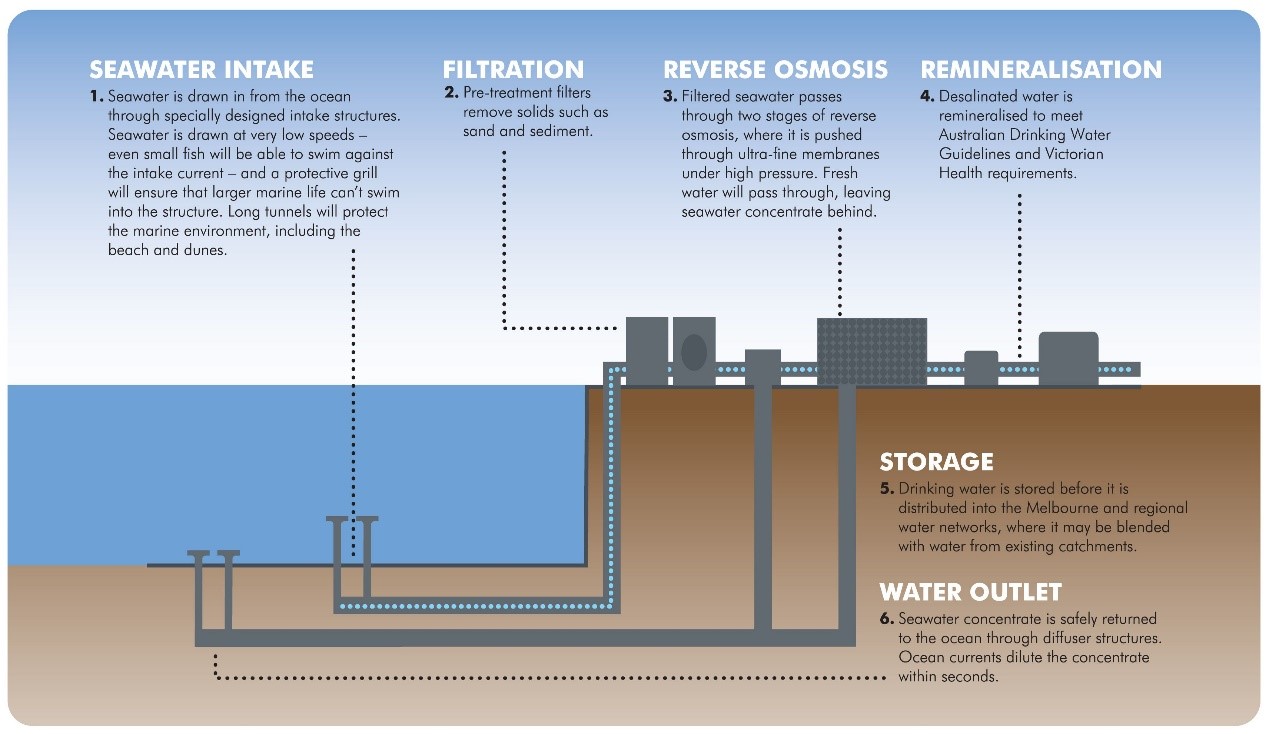
Desalination of Seawater and Brackish Water:
RO is commonly used to desalinate seawater and brackish water, producing fresh water for drinking, industrial processes, and agriculture.
Production of Pure and Ultra-Pure Water:
RO membranes are employed in producing pure water for laboratories, electronics manufacturing, pharmaceuticals, and other high-purity applications.
Ultra-pure water is essential in semiconductor fabrication, where even trace impurities can affect performance.
Industrial Water Treatment:
RO systems treat industrial process water, including wastewater recycling, boiler feedwater, and cooling tower makeup water.
It removes dissolved salts, heavy metals, and other contaminants.
Food and Beverage Industry:
RO concentrates fruit juices, syrups, and other liquids without damaging proteins and enzymes.
It ensures consistent water quality for food and beverage production.
Environmental Remediation:
RO helps clean up polluted streams, removing contaminants and improving water quality.
It is an effective method for treating industrial effluents.
Chemical Separations:
RO can be used as a pre-separation step in chemical assays.
It concentrates solutes from solvents prior to analysis.
Remember that RO technology is widely used in various fields, including research, medicine, food, beverages, and seawater desalination. If you have any more questions or need further details, feel free to ask us.